Lists
We've so far covered how to render many Futures (we rendered 100 <span>s in chapter 1),
and how to dynamically put or remove a Future (the previous subchapter on DynamicSlot).
Now, how do we dynamically insert or remove from a list of many Futures?
Async UI comes with many different list components. They are documented here.
The most recommended list - the one we will use in this guide - is ModeledList.
Each ModeledList has two parts:
- The
ModeledListinstance. This is what you.render(). It knows how to turn each list item into a Future to be rendered. - The data model: ListModel.
This is where the items of the list actually live. It is similar to a
Vec.
Operation is simple: you update the ListModel,
then tell the ModeledList that the data have been updated,
and the ModeledList will figure out inserting new items and deleting removed items.
Example: a Fibonacci list
We'll make a list of Fibonacci numbers. First, let's import things
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use async_ui_web::{ html::Div, join, lists::{ListModel, ModeledList}, // 👈 new! shortcut_traits::ShortcutRenderStr, }; use gloo_timers::future::TimeoutFuture; }
Before making the list, let's think of how we'll render each item in the list
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { async fn render_one_item(n: usize, fib_n: u64) { Div::new() .render(format!("The {n}th Fibonacci number is {fib_n}.").render()) .await; } }
And finally, we make the list
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { async fn fibonacci() { // 👇 create a list that can render numbers let list = ModeledList::new(|(n, fib_n)| render_one_item(*n, *fib_n)); // 👇 create a model that contains the numbers we'll render let mut fibo = ListModel::from(vec![ (1, 1), // fib_1 is 1 (2, 1), // fib_2 is also 1 ]); // 👇 tell the list to render the numbers in the `fibo` model list.update(&fibo); // join 2 Futures: // * the list // * a Future to manipulate the items join(( list.render(), // 👈 render the list async { loop { // wait 1 second TimeoutFuture::new(1000).await; // 👇 change `fibo`, adding the next fibonacci number fibo.push(( fibo.len() + 1, // `n` - the index of the next fibo number // compute `fib_n` fibo.iter() .rev() .map(|(_n, fib_n)| fib_n) .take(2) .cloned() .sum(), )); // 👇 tell the list that the numbers in the model have changed list.update(&fibo); } }, )) .await; } }
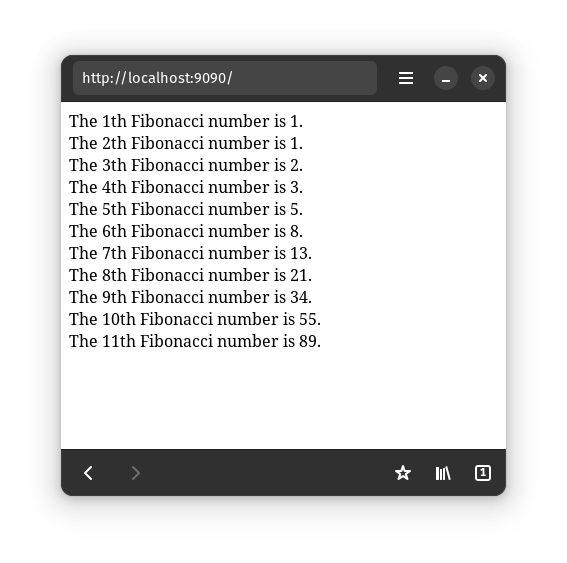
Warning: Our Fibonacci implementation will eventually overflow.
Fixing the incorrect English usage ("1th", "2th", "3th") is left as an exercise for the reader.